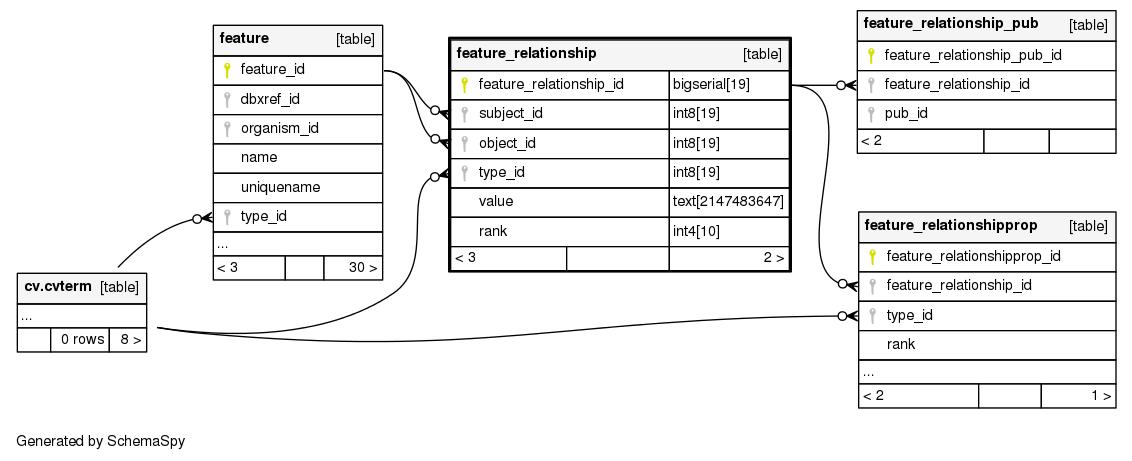
Columns
| Column | Type | Size | Foreign Key | Nullable | Default | Comments | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| feature_relationship_id | bigserial | 19 |
|
nextval('sequence.feature_relationship_feature_relationship_id_seq'::regclass) | ||||
| subject_id | int8 | 19 |
|
null | The subject of the subj-predicate-obj sentence. This is typically the subfeature. |
|||
| object_id | int8 | 19 |
|
null | The object of the subj-predicate-obj sentence. This is typically the container feature. |
|||
| type_id | int8 | 19 |
|
null | Relationship type between subject and object. This is a cvterm, typically from the OBO relationship ontology, although other relationship types are allowed. The most common relationship type is OBO_REL:part_of. Valid relationship types are constrained by the Sequence Ontology. |
|||
| value | text | 2147483647 |
|
√ | null | Additional notes or comments. |
||
| rank | int4 | 10 |
|
0 | The ordering of subject features with respect to the object feature may be important (for example, exon ordering on a transcript - not always derivable if you take trans spliced genes into consideration). Rank is used to order these; starts from zero. |
Table contained -1 rows
Indexes
| Constraint Name | Type | Sort | Column(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| feature_relationship_pkey | Primary key | Asc | feature_relationship_id |
| feature_relationship_c1 | Must be unique | Asc/Asc/Asc/Asc | subject_id + object_id + type_id + rank |
| feature_relationship_idx1 | Performance | Asc | subject_id |
| feature_relationship_idx2 | Performance | Asc | object_id |
| feature_relationship_idx3 | Performance | Asc | type_id |